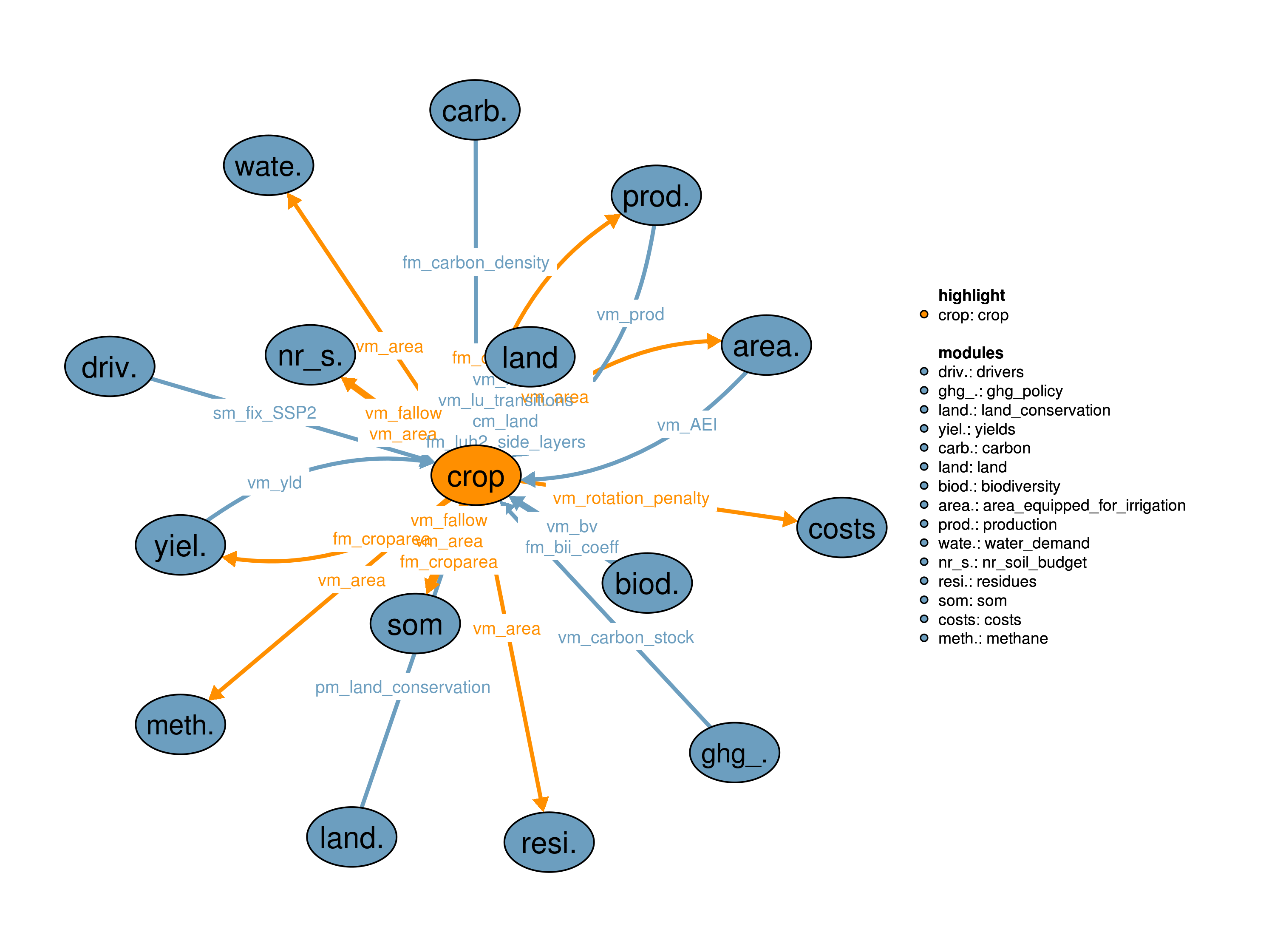
The cropland module simulates the dynamics of cropland area and agricultural crop production and calculates corresponding carbon contents and the biodiversity value of the existing cropland.
| Description | Unit | A | B | C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fm_bii_coeff (bii_class44, potnatveg) |
Biodiversity Intactness Index coefficients | \(unitless\) | x | x | x |
| fm_carbon_density (t_all, j, land, c_pools) |
LPJmL carbon density for land and carbon pools | \(tC/ha\) | x | x | x |
| fm_luh2_side_layers (j, luh2_side_layers10) |
luh2 side layers | \(grid cell share\) | x | x | x |
| pcm_land (j, land) |
Land area in previous time step including possible changes after optimization | \(10^6 ha\) | x | x | x |
| pm_land_conservation (t, j, land, consv_type) |
Land protection and restoration for all land types | \(10^6 ha\) | x | x | x |
| sm_fix_SSP2 | year until which all parameters are fixed to SSP2 values | \(year\) | x | x | x |
| vm_AEI (j) |
Area equipped for irrigation in each grid cell | \(10^6 ha\) | x | x | |
| vm_bv (j, landcover44, potnatveg) |
Biodiversity stock for all land cover classes | \(Mha\) | x | x | x |
| vm_carbon_stock (j, land, c_pools, stockType) |
Carbon stock in vegetation soil and litter for different land types | \(10^6 tC\) | x | x | x |
| vm_land (j, land) |
Land area of the different land types | \(10^6 ha\) | x | x | x |
| vm_lu_transitions (j, land_from, land_to) |
Land transitions between time steps | \(10^6 ha\) | x | x | x |
| vm_prod (j, k) |
Production in each cell | \(10^6 tDM/yr\) | x | x | x |
| vm_yld (j, kve, w) |
Yields (variable because of technical change) | \(tDM/ha/yr\) | x | x | x |
| Description | Unit | |
|---|---|---|
| fm_croparea (t_all, j, w, kcr) |
Different croparea type areas | \(10^6 ha\) |
| vm_area (j, kcr, w) |
Agricultural production area | \(10^6 ha\) |
| vm_fallow (j) |
Fallow land | \(10^6 ha\) |
| vm_rotation_penalty (i) |
Penalty for violating rotational constraints | \(USD_{05MER}\) |
The endo_apr21 realization calculates the crop specific agricultural land use endogenously based on yield data coming from the module 14_yields and the rotational as well as suitability constraints stated in the input data of the module.
Cropland areas are linked to the crop specific production and the carbon content of the different land carbon pools. The crop specific land use areas are also used in 18_residues, 38_factor_costs, 41_area_equipped_for_irrigation, 42_water_demand, 50_nr_soil_budget, 53_methane and 59_som. This realisation also includes the option to reserve a minimum semi-natural vegetation share within the total available cropland for other land cover classes, including grassland, forest, and other land (by a given target year), in order to provide species habitats and to benefit from ecosystem ervices in agricultural landscapes.
The total land requirements for cropland are calculated as the sum of crop and water supply type specific land requirements:
\[\begin{multline*} \sum_{kcr,w} vm\_area(j2,kcr,w) = vm\_land(j2,"crop") \end{multline*}\]
We assume that crop production can only take place on suitable cropland area. We use a suitability index (SI) map from Zabel, Putzenlechner, and Mauser (2014) to exclude areas from cropland production that have a low suitability, e.g. due to steep slopes, to estimate the available cropland area. The cultivated area therefore has to be smaller than the available cropland area. Moreover, the available cropland can be reduced by constraining the cropland area in favour of other land types, in order to increase compositional heterogeneity of land types at the cell level.
\[\begin{multline*} vm\_land(j2,"crop") \leq \sum_{ct} p30\_avl\_cropland(ct,j2) \end{multline*}\]
The semi-natural land constraint in cropland areas for sustaining critical regulating NCP for agricultural production is added on top of land conserved for other reasons (e.g. conservation of intact ecosystems or protection of biodiversity hotspots).
\[\begin{multline*} \sum_{land\_snv} vm\_land(j2,land\_snv) \geq \sum_{ct} p30\_snv\_shr(ct,j2) \cdot vm\_land(j2,"crop") + \sum_{ct,land\_snv,consv\_type} pm\_land\_conservation(ct,j2,land\_snv,consv\_type) \end{multline*}\]
The semi-natural vegetation constraint for cropland areas has been suggested at the per square kilometer scale. The amount of cropland requiring relocation has therefore been derived from exogeneous high-resolution land cover information from the Copernicus Global Land Service (Buchhorn et al. (2020)).
\[\begin{multline*} \sum_{land\_snv} vm\_lu\_transitions(j2,"crop",land\_snv) \geq \sum_{ct} p30\_snv\_relocation(ct,j2) \end{multline*}\]
As additional constraints minimum and maximum rotational constraints limit the placing of crops. On the one hand, these rotational constraints reflect crop rotations limiting the share a specific crop can cover of the total area of a cluster:
\[\begin{multline*} \sum_{crp\_kcr30(crpmax30,kcr)} vm\_area(j2,kcr,w) \leq \sum_{kcr} vm\_area(j2,kcr,w) \cdot f30\_rotation\_max\_shr(crpmax30) \end{multline*}\]
On the other hand, it reflects boundary conditions such as minimum self sufficiency constraints:
\[\begin{multline*} \sum_{crp\_kcr30(crpmin30,kcr)} vm\_area(j2,kcr,w) \geq \sum_{kcr} vm\_area(j2,kcr,w) \cdot f30\_rotation\_min\_shr(crpmin30) \end{multline*}\]
Agricultural production is calculated by multiplying the area under production with corresponding yields. Production from rainfed and irrigated areas is summed up:
\[\begin{multline*} vm\_prod(j2,kcr) = \sum_{w}\left( vm\_area(j2,kcr,w) \cdot vm\_yld(j2,kcr,w)\right) \end{multline*}\]
The carbon content of the above ground carbon pools are calculated as a total for all cropland :
\[\begin{multline*} vm\_carbon\_stock(j2,"crop",ag\_pools,stockType) = m\_carbon\_stock(vm\_land,fm\_carbon\_density,"crop") \end{multline*}\]
The biodiversity value for cropland is calculated separately for annual and perennial crops:
\[\begin{multline*} vm\_bv(j2,"crop\_ann",potnatveg) = \sum_{crop\_ann30,w} vm\_area(j2,crop\_ann30,w) \cdot fm\_bii\_coeff("crop\_ann",potnatveg) \cdot fm\_luh2\_side\_layers(j2,potnatveg) \end{multline*}\]
\[\begin{multline*} vm\_bv(j2,"crop\_per",potnatveg) = \left(vm\_land(j2,"crop") - \sum_{crop\_ann30,w} vm\_area(j2,crop\_ann30,w)\right) \cdot fm\_bii\_coeff("crop\_per",potnatveg) \cdot fm\_luh2\_side\_layers(j2,potnatveg) \end{multline*}\]
First, all 2nd generation bioenergy area is fixed to zero, irrespective of type and rainfed/irrigation.
vm_area.fx(j,kbe30,w)=0;Second, the bounds for 2nd generation bioenergy area are released depending on the dynamic sets bioen_type_30 and bioen_water_30. SSP2 default settings are used for the historic period.
if(m_year(t) <= sm_fix_SSP2,
vm_area.up(j,kbe30,"rainfed") = Inf;
else
vm_area.up(j,bioen_type_30,bioen_water_30) = Inf;
);Minimum semi-natural vegetation (SNV) share is fading in after 2020
p30_snv_shr(t,j) = p30_snv_scenario_fader(t) *
(s30_snv_shr * sum(cell(i,j), p30_country_snv_weight(i))
+ s30_snv_shr_noselect * sum(cell(i,j), 1-p30_country_snv_weight(i)));Cropland relocation in response to SNV policy is based on exogeneous land cover information from the Copernicus Global Land Service (Buchhorn et al. (2020)). The rate of the policy implementation is derived based on the difference of scenario fader values in consecutive time steps
p30_snv_relocation(t,j) = (p30_snv_scenario_fader(t) - p30_snv_scenario_fader(t-1)) *
(i30_snv_relocation_target(j) * sum(cell(i,j), p30_country_snv_weight(i))
+ s30_snv_shr_noselect * sum(cell(i,j), 1-p30_country_snv_weight(i)));The following lines take care of mismatches in the input data (derived from satellite imagery from the Copernicus Global Land Service (Buchhorn et al. (2020))) and in cases of cropland reduction
p30_max_snv_relocation(t,j) = p30_snv_shr(t,j) * (p30_snv_scenario_fader(t) - p30_snv_scenario_fader(t-1)) * pcm_land(j,"crop");
p30_snv_relocation(t,j)$(p30_snv_relocation(t, j) > p30_max_snv_relocation(t,j)) = p30_max_snv_relocation(t,j);Area potentially available for cropping
p30_avl_cropland(t,j) = f30_avl_cropland(j,"%c30_marginal_land%") * (1 - p30_snv_shr(t,j));Limitations There are currently no known limitations of this realization.
The endo_apr21 realization calculates the crop specific agricultural land use endogenously based on yield data coming from the module 14_yields and the rotational incentives as well as suitability constraints stated in the input data of the module.
Cropland areas are linked to the crop specific production and the carbon content of the different land carbon pools. The crop specific land use areas are also used in 18_residues, 38_factor_costs, 41_area_equipped_for_irrigation, 42_water_demand, 50_nr_soil_budget, 53_methane and 59_som. This module realization allows for different scenarios of rotational constraints which are implemented via penalty payments if constraints are exceeded. Rotational constraints are defined for total land as well as for irrigated areas only to avoid overspecialization on irrigated land. This realisation also includes the option to reserve a minimum semi-natural vegetation share within the total available cropland for other land cover classes, including grassland, forest, and other land (by a given target year), in order to provide species habitats and to benefit from ecosystem ervices in agricultural landscapes.
The total land requirements for cropland are calculated as the sum of crop and water supply type specific land requirements. Fallow is no explicit landuse type, but the difference between the land area for crops vm_land and the croparea vm_area
\[\begin{multline*} \sum_{kcr,w} vm\_area(j2,kcr,w) + vm\_fallow(j2) = vm\_land(j2,"crop") \end{multline*}\]
We assume that crop production can only take place on suitable cropland area. We use a suitability index (SI) map from Zabel, Putzenlechner, and Mauser (2014) to exclude areas from cropland production that have a low suitability, e.g. due to steep slopes, to estimate the available cropland area. The cultivated area therefore has to be smaller than the available cropland area. Moreover, the available cropland can be reduced by constraining the cropland area in favour of other land types, in order to increase compositional heterogeneity of land types at the cell level.
\[\begin{multline*} vm\_land(j2,"crop") \leq \sum_{ct} p30\_avl\_cropland(ct,j2) \end{multline*}\]
The semi-natural land constraint in cropland areas for sustaining critical regulating NCP for agricultural production is added on top of land conserved for other reasons (e.g. conservation of intact ecosystems or protection of biodiversity hotspots).
\[\begin{multline*} \sum_{land\_snv} vm\_land(j2,land\_snv) \geq \sum_{ct} p30\_snv\_shr(ct,j2) \cdot vm\_land(j2,"crop") + \sum_{ct,land\_snv,consv\_type} pm\_land\_conservation(ct,j2,land\_snv,consv\_type) \end{multline*}\]
The semi-natural vegetation constraint for cropland areas has been suggested at the per square kilometer scale. The amount of cropland requiring relocation has therefore been derived from exogeneous high-resolution land cover information from the Copernicus Global Land Service (Buchhorn et al. (2020)).
\[\begin{multline*} \sum_{land\_snv} vm\_lu\_transitions(j2,"crop",land\_snv) \geq \sum_{ct} p30\_snv\_relocation(ct,j2) \end{multline*}\]
Rotational constraints prevent over-specialization. In this module realization, they are implemented via a penalty payment if the constraints are violated.
\[\begin{multline*} vm\_rotation\_penalty(i2) \geq \sum_{cell(i2,j2)}\left( \sum_{rota30}\left( v30\_penalty(j2,rota30) \cdot \sum_{ct} i30\_rotation\_incentives(ct,rota30)\right) + \sum_{rotamax\_red30}\left( v30\_penalty\_max\_irrig(j2,rotamax\_red30) \cdot \sum_{ct} i30\_rotation\_incentives(ct,rotamax\_red30)\right) \right) \end{multline*}\]
The penalty applies to the areas which exceed a certain maximum share of the land. Below this share, negative benefits are avoided by defining the penalty to be positive.
\[\begin{multline*} v30\_penalty(j2,rotamax\_red30) \geq \sum_{rota\_kcr30(rotamax\_red30,kcr),w}vm\_area(j2,kcr,w) - vm\_land(j2,"crop") \cdot f30\_rotation\_rules(rotamax\_red30) \end{multline*}\]
Minimum constraints apply penalties when a certain mimimum share of a group is not achieved. This is used to guarantee a minimum crop group diversity withing cells.
\[\begin{multline*} v30\_penalty(j2,rotamin\_red30) \geq vm\_land(j2,"crop") \cdot f30\_rotation\_rules(rotamin\_red30) - \sum_{rota\_kcr30(rotamin\_red30,kcr),w} vm\_area(j2,kcr,w) \end{multline*}\]
The following maximum constraint avoids over-specialization in irrigated systems. No minimum constraint is included for irrigated areas for computational reasons. Minimum constraints just need to be met on total areas.
\[\begin{multline*} v30\_penalty\_max\_irrig(j2,rotamax\_red30) \geq \sum_{rota\_kcr30(rotamax\_red30,kcr)} vm\_area(j2,kcr,"irrigated") - vm\_AEI(j2) \cdot f30\_rotation\_rules(rotamax\_red30) \end{multline*}\]
Agricultural production is calculated by multiplying the area under production with corresponding yields. Production from rainfed and irrigated areas is summed up:
\[\begin{multline*} vm\_prod(j2,kcr) = \sum_{w}\left( vm\_area(j2,kcr,w) \cdot vm\_yld(j2,kcr,w)\right) \end{multline*}\]
The carbon content of the above ground carbon pools are calculated as a total for all cropland :
\[\begin{multline*} vm\_carbon\_stock(j2,"crop",ag\_pools,stockType) = m\_carbon\_stock(vm\_land,fm\_carbon\_density,"crop") \end{multline*}\]
The biodiversity value for cropland is calculated separately for annual and perennial crops:
\[\begin{multline*} vm\_bv(j2,"crop\_ann",potnatveg) = \sum_{crop\_ann30,w} vm\_area(j2,crop\_ann30,w) \cdot fm\_bii\_coeff("crop\_ann",potnatveg) \cdot fm\_luh2\_side\_layers(j2,potnatveg) \end{multline*}\]
perennial crops are calculated as difference, as they shall also include fallow land
\[\begin{multline*} vm\_bv(j2,"crop\_per",potnatveg) = \left(vm\_land(j2,"crop") - \sum_{crop\_ann30,w} vm\_area(j2,crop\_ann30,w)\right) \cdot fm\_bii\_coeff("crop\_per",potnatveg) \cdot fm\_luh2\_side\_layers(j2,potnatveg) \end{multline*}\]
First, all 2nd generation bioenergy area is fixed to zero, irrespective of type and rainfed/irrigation.
vm_area.fx(j,kbe30,w)=0;Second, the bounds for 2nd generation bioenergy area are released depending on the dynamic sets bioen_type_30 and bioen_water_30. SSP2 default settings are used for the historic period.
if(m_year(t) <= sm_fix_SSP2,
vm_area.up(j,kbe30,"rainfed") = Inf;
else
vm_area.up(j,bioen_type_30,bioen_water_30) = Inf;
);Minimum semi-natural vegetation (SNV) share is fading in after 2020
p30_snv_shr(t,j) = p30_snv_scenario_fader(t) *
(s30_snv_shr * sum(cell(i,j), p30_country_snv_weight(i))
+ s30_snv_shr_noselect * sum(cell(i,j), 1-p30_country_snv_weight(i)));Cropland relocation in response to SNV policy is based on exogeneous land cover information from the Copernicus Global Land Service (Buchhorn et al. (2020)). The rate of the policy implementation is derived based on the difference of scenario fader values in consecutive time steps
p30_snv_relocation(t,j) = (p30_snv_scenario_fader(t) - p30_snv_scenario_fader(t-1)) *
(i30_snv_relocation_target(j) * sum(cell(i,j), p30_country_snv_weight(i))
+ s30_snv_shr_noselect * sum(cell(i,j), 1-p30_country_snv_weight(i)));The following lines take care of mismatches in the input data (derived from satellite imagery from the Copernicus Global Land Service (Buchhorn et al. (2020))) and in cases of cropland reduction
p30_max_snv_relocation(t,j) = p30_snv_shr(t,j) * (p30_snv_scenario_fader(t) - p30_snv_scenario_fader(t-1)) * pcm_land(j,"crop");
p30_snv_relocation(t,j)$(p30_snv_relocation(t, j) > p30_max_snv_relocation(t,j)) = p30_max_snv_relocation(t,j);Area potentially available for cropping
p30_avl_cropland(t,j) = f30_avl_cropland(j,"%c30_marginal_land%") * (1 - p30_snv_shr(t,j));Limitations There are currently no known limitations of this realization.
The rotation_apr21 realization calculates the crop specific agricultural land use endogenously based on yield data coming from the module 14_yields and the rotational as well as suitability constraints stated in the input data of the module.
Cropland areas are linked to the crop specific production and the carbon content of the different land carbon pools. The crop specific land use areas are also used in 18_residues, 38_factor_costs, 41_area_equipped_for_irrigation, 42_water_demand, 50_nr_soil_budget, 53_methane and 59_som. This module realization allows for different scenarios of rotational constraints. These are implemented as hard constraints. Maximum rotational constraints are defined for total cropland as well as for irrigated areas only to avoid overspecialization on irrigated land. Minimum constraints are just valid for total cropland areas. This realisation also includes the option to reserve a minimum semi-natural vegetation share within the total available cropland for other land cover classes, including grassland, forest, and other land (by a given target year), in order to provide species habitats and to benefit from ecosystem ervices in agricultural landscapes.
The total land requirements for cropland are calculated as the sum of crop and water supply type specific land requirements: Fallow is no explicit landuse type, but the difference between the land area for crops vm_land and the croparea vm_area
\[\begin{multline*} \sum_{kcr,w} vm\_area(j2,kcr,w) + vm\_fallow(j2) = vm\_land(j2,"crop") \end{multline*}\]
We assume that crop production can only take place on suitable cropland area. We use a suitability index (SI) map from Zabel, Putzenlechner, and Mauser (2014) to exclude areas from cropland production that have a low suitability, e.g. due to steep slopes, to estimate the available cropland area. The cultivated area therefore has to be smaller than the available cropland area. Moreover, the available cropland can be reduced by constraining the cropland area in favour of other land types, in order to increase compositional heterogeneity of land types at the cell level.
\[\begin{multline*} vm\_land(j2,"crop") \leq \sum_{ct} p30\_avl\_cropland(ct,j2) \end{multline*}\]
The semi-natural land constraint in cropland areas for sustaining critical regulating NCP for agricultural production is added on top of land conserved for other reasons (e.g. conservation of intact ecosystems or protection of biodiversity hotspots).
\[\begin{multline*} \sum_{land\_snv} vm\_land(j2,land\_snv) \geq \sum_{ct} p30\_snv\_shr(ct,j2) \cdot vm\_land(j2,"crop") + \sum_{ct,land\_snv,consv\_type} pm\_land\_conservation(ct,j2,land\_snv,consv\_type) \end{multline*}\]
The semi-natural vegetation constraint for cropland areas has been suggested at the per square kilometer scale. The amount of cropland requiring relocation has therefore been derived from exogeneous high-resolution land cover information from the Copernicus Global Land Service (Buchhorn et al. (2020)).
\[\begin{multline*} \sum_{land\_snv} vm\_lu\_transitions(j2,"crop",land\_snv) \geq \sum_{ct} p30\_snv\_relocation(ct,j2) \end{multline*}\]
As additional constraints minimum and maximum rotational constraints limit the placing of crops. On the one hand, these rotational constraints reflect crop rotations limiting the share a specific crop can cover of the total area of a cluster:
\[\begin{multline*} \sum_{rotamax\_kcr30(rotamax\_red30,kcr),w} vm\_area(j2,kcr,w) \leq vm\_land(j2,"crop") \cdot \sum_{ct}i30\_rotation\_max\_shr(ct,rotamax\_red30) \end{multline*}\]
\[\begin{multline*} \sum_{rotamin\_kcr30(rotamin\_red30,kcr),w} vm\_area(j2,kcr,w) \geq vm\_land(j2,"crop") \cdot \sum_{ct}i30\_rotation\_min\_shr(ct,rotamin\_red30) \end{multline*}\]
\[\begin{multline*} \sum_{rotamax\_kcr30(rotamax\_red30,kcr)} vm\_area(j2,kcr,"irrigated") \leq vm\_AEI(j2) \cdot \sum_{ct}i30\_rotation\_max\_shr(ct,rotamax\_red30) \end{multline*}\]
Agricultural production is calculated by multiplying the area under production with corresponding yields. Production from rainfed and irrigated areas is summed up:
\[\begin{multline*} vm\_prod(j2,kcr) = \sum_{w}\left( vm\_area(j2,kcr,w) \cdot vm\_yld(j2,kcr,w)\right) \end{multline*}\]
The carbon content of the above ground carbon pools are calculated as a total for all cropland :
\[\begin{multline*} vm\_carbon\_stock(j2,"crop",ag\_pools,stockType) = m\_carbon\_stock(vm\_land,fm\_carbon\_density,"crop") \end{multline*}\]
The biodiversity value for cropland is calculated separately for annual and perennial crops:
\[\begin{multline*} vm\_bv(j2,"crop\_ann",potnatveg) = \sum_{crop\_ann30,w} vm\_area(j2,crop\_ann30,w) \cdot fm\_bii\_coeff("crop\_ann",potnatveg) \cdot fm\_luh2\_side\_layers(j2,potnatveg) \end{multline*}\]
\[\begin{multline*} vm\_bv(j2,"crop\_per",potnatveg) = \left(vm\_land(j2,"crop") - \sum_{crop\_ann30,w} vm\_area(j2,crop\_ann30,w)\right) \cdot fm\_bii\_coeff("crop\_per",potnatveg) \cdot fm\_luh2\_side\_layers(j2,potnatveg) \end{multline*}\]
First, all 2nd generation bioenergy area is fixed to zero, irrespective of type and rainfed/irrigation.
vm_area.fx(j,kbe30,w)=0;Second, the bounds for 2nd generation bioenergy area are released depending on the dynamic sets bioen_type_30 and bioen_water_30. SSP2 default settings are used for the historic period.
if(m_year(t) <= sm_fix_SSP2,
vm_area.up(j,kbe30,"rainfed") = Inf;
else
vm_area.up(j,bioen_type_30,bioen_water_30) = Inf;
);Minimum semi-natural vegetation (SNV) share is fading in after 2020
p30_snv_shr(t,j) = p30_snv_scenario_fader(t) *
(s30_snv_shr * sum(cell(i,j), p30_country_snv_weight(i))
+ s30_snv_shr_noselect * sum(cell(i,j), 1-p30_country_snv_weight(i)));Cropland relocation in response to SNV policy is based on exogeneous land cover information from the Copernicus Global Land Service (Buchhorn et al. (2020)). The rate of the policy implementation is derived based on the difference of scenario fader values in consecutive time steps
p30_snv_relocation(t,j) = (p30_snv_scenario_fader(t) - p30_snv_scenario_fader(t-1)) *
(i30_snv_relocation_target(j) * sum(cell(i,j), p30_country_snv_weight(i))
+ s30_snv_shr_noselect * sum(cell(i,j), 1-p30_country_snv_weight(i)));The following lines take care of mismatches in the input data (derived from satellite imagery) and in cases of cropland reduction
p30_max_snv_relocation(t,j) = p30_snv_shr(t,j) * (p30_snv_scenario_fader(t) - p30_snv_scenario_fader(t-1)) * pcm_land(j,"crop");
p30_snv_relocation(t,j)$(p30_snv_relocation(t, j) > p30_max_snv_relocation(t,j)) = p30_max_snv_relocation(t,j);Area potentially available for cropping
p30_avl_cropland(t,j) = f30_avl_cropland(j,"%c30_marginal_land%") * (1 - p30_snv_shr(t,j));Limitations There are currently no known limitations of this realization.
| Description | Unit | A | B | C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| f30_avl_cropland (j, marginal_land30) |
Available land area for cropland | \(10^6 ha\) | x | x | x |
| f30_avl_cropland_iso (iso, marginal_land30) |
Available land area for cropland at ISO level | \(10^6 ha\) | x | x | x |
| f30_rotation_incentives (rota30, rotascen30) |
penalties for violating rotation rules | \(USD_{05MER}\) | x | ||
| f30_rotation_max_shr (crp30) |
Maximum allowed area shares for each crop type | \(1\) | x | x | |
| f30_rotation_min_shr (crp30) |
Minimum allowed area shares for each crop type | \(1\) | x | x | |
| f30_rotation_rules (rota30) |
Rotation min or max shares | \(1\) | x | ||
| f30_snv_target_cropland (j, relocation_target30) |
Cropland in 2019 requiring relocation due to SNV policy | \(10^6 ha\) | x | x | x |
| i30_avl_cropland_iso (iso) |
Available land area for cropland at ISO level | \(10^6 ha\) | x | x | x |
| i30_rotation_incentives (t_all, rota30) |
Penalty for violating rotational constraints | \(USD_{05MER}/ha\) | x | ||
| i30_rotation_max_shr (t_all, rotamax30) |
Maximum share of a certain crop group on cropland | \(ha/ha\) | x | ||
| i30_rotation_min_shr (t_all, rotamin30) |
Minimum share of a certain crop group on cropland | \(ha/ha\) | x | ||
| i30_snv_relocation_target (j) |
Overall cropland area that requires relocation due to SNV policy | \(10^6 ha\) | x | x | x |
| p30_avl_cropland (t, j) |
Total available land for crop cultivation | \(10^6 ha\) | x | x | x |
| p30_country_dummy (iso) |
Dummy parameter indicating whether country is affected by selected cropland policy | \(1\) | x | x | x |
| p30_country_snv_weight (i) |
SNV policy country weight per region | \(1\) | x | x | x |
| p30_max_snv_relocation (t, j) |
Maximum cropland relocation during time step | \(10^6 ha\) | x | x | x |
| p30_rotation_scenario_fader (t_all) |
Crop rotation scenario fader | \(1\) | x | x | x |
| p30_snv_relocation (t, j) |
Cropland area that is actually relocated during time step | \(10^6 ha\) | x | x | x |
| p30_snv_scenario_fader (t_all) |
SNV scenario fader | \(1\) | x | x | x |
| p30_snv_shr (t, j) |
Share of semi-natural vegetation in cropland areas | \(1\) | x | x | x |
| q30_avl_cropland (j) |
Available cropland constraint | \(10^6 ha\) | x | x | x |
| q30_bv_ann (j, potnatveg) |
Biodiversity value of annual cropland | \(10^6 ha\) | x | x | x |
| q30_bv_per (j, potnatveg) |
Biodiversity value of perennial cropland | \(10^6 ha\) | x | x | x |
| q30_carbon (j, ag_pools, stockType) |
Cropland above ground carbon content calculation | \(10^6 tC\) | x | x | x |
| q30_cropland (j) |
Total cropland calculation | \(10^6 ha\) | x | x | x |
| q30_land_snv (j) |
Land constraint for the SNV policy in cropland areas | \(10^6 ha\) | x | x | x |
| q30_land_snv_trans (j) |
Land transition constraint for SNV policy in cropland areas | \(10^6 ha\) | x | x | x |
| q30_prod (j, kcr) |
Production of cropped products | \(10^6 tDM\) | x | x | x |
| q30_rotation_max (j, crp30, w) |
Local maximum rotational constraints | \(10^6 ha\) | x | x | x |
| q30_rotation_max_irrig (j, rotamax30) |
Local maximum rotational constraints | \(10^6 ha\) | x | x | |
| q30_rotation_min (j, crp30, w) |
Local minimum rotational constraints | \(10^6 ha\) | x | x | x |
| q30_rotation_penalty (i) |
Total penalty for rotational constraint violations | \(10^6 USD_{05MER}\) | x | ||
| s30_rotation_scenario_start | Rotation scenario start year | x | x | x | |
| s30_rotation_scenario_target | Rotation scenario target year | x | x | x | |
| s30_snv_relocation_data_x1 | First reference value in SNV target cropland data | \(1\) | x | x | x |
| s30_snv_relocation_data_x2 | Second reference value in SNV target cropland data | \(1\) | x | x | x |
| s30_snv_scenario_start | SNV scenario start year | x | x | x | |
| s30_snv_scenario_target | SNV scenario target year | x | x | x | |
| s30_snv_shr | Share of available cropland that is witheld for other land cover types | \(1\) | x | x | x |
| s30_snv_shr_noselect | Share of available cropland that is witheld for other land cover types | \(1\) | x | x | x |
| v30_penalty (j, rota30) |
Penalty for violating rotational constraints | \(10^6 USD_{05MER}\) | x | ||
| v30_penalty_max_irrig (j, rotamax30) |
Penalty for violating max rotational constraints on irrigated land | \(10^6 USD_{05MER}\) | x |
| description | |
|---|---|
| ag_pools(c_pools) | Above ground carbon pools |
| bii_class44 | bii coefficent land cover classes |
| bioen_type_30(kbe30) | dynamic set bioen type |
| bioen_water_30(w) | dynamic set bioen water |
| c_pools | Carbon pools |
| cell(i, j) | number of LPJ cells per region i |
| consv_type | Type of land conservation |
| crop_ann30(kcr) | annual crops |
| crop_per30(kcr) | perennial crops |
| crp_kcr30(crp30, kcr) | Mapping of crop types into crop rotation types |
| crp30 | Crop rotation types |
| crpmax30(crp30) | Maximum crop rotation |
| crpmin30(crp30) | Minimum crop rotation |
| ct(t) | Current time period |
| i | all economic regions |
| i_to_iso(i, iso) | mapping regions to iso countries |
| i2(i) | World regions (dynamic set) |
| iso | list of iso countries |
| j | number of LPJ cells |
| j2(j) | Spatial Clusters (dynamic set) |
| k(kall) | Primary products |
| kbe30(kcr) | bio energy activities |
| kcr(kve) | Cropping activities |
| kve(k) | Land-use activities |
| land | Land pools |
| land_snv(land) | land types allowed in the SNV policy |
| landcover44 | land cover classes used in bii calculation |
| luh2_side_layers10 | side layers from LUH2 |
| marginal_land30 | Marginal land scenarios |
| policy_countries30(iso) | countries to be affected by SNV policy |
| policy_target30 | Target year for cropland policy |
| potnatveg(luh2_side_layers10) | potentially forested biomes |
| relocation_target30 | Cropland requiring relocation based on different SNV targets |
| rota_kcr30(rota30, kcr) | Mapping of crop types into crop rotation types |
| rota30 | rotational rules |
| rotamax_kcr30(rotamax30, kcr) | Mapping of crop types into crop rotation types |
| rotamax_red30(rotamax30) | Maximum crop rotation reduced set |
| rotamax30(rota30) | rotational maximum rules |
| rotamin_kcr30(rotamin30, kcr) | Mapping of crop types into crop rotation types |
| rotamin_red30(rotamin30) | Minimum crop rotation reduced set |
| rotamin30(rota30) | rotational minimum rules |
| rotascen30 | rotation constraint scenarios |
| stockType | Carbon stock types |
| t_all(t_ext) | 5-year time periods |
| t_past(t_all) | Timesteps with observed data |
| t(t_all) | Simulated time periods |
| type | GAMS variable attribute used for the output |
| w | Water supply type |
Jan Philipp Dietrich, Florian Humpenöder, Benjamin Bodirsky
09_drivers, 10_land, 11_costs, 14_yields, 17_production, 18_residues, 22_land_conservation, 41_area_equipped_for_irrigation, 42_water_demand, 44_biodiversity, 50_nr_soil_budget, 52_carbon, 53_methane, 56_ghg_policy, 59_som